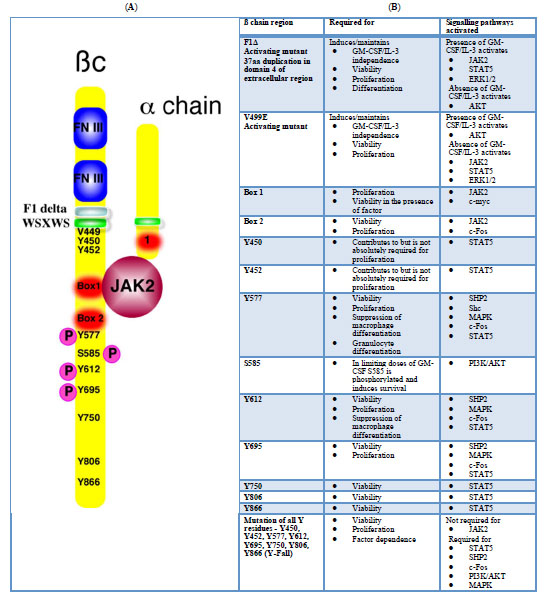
Fig. (1) A. The GM-CSF/IL-3/IL-5 receptor is a heterodimer of a specific alpha chain and a common beta chain (ßc). The extracellular domain of the ßc has two fibronectin type III repeats involved in IL-3/GM-CSF binding. The ßc also has a WSXWS transmembrane domain. Activating mutations of ßc have been identified in the transmembrane domain (e.g. V449E and F1Δ [40]). The cytosolic portion of ßc contains a Box 1 and Box 2 motifs, involved in JAK binding and activation. Deletion of these domains abolishes signalling. A number of tyrosine residues are phosphorylated after ligand binding. Tyrosines (Y) 577, 612 and 690 are all involved in the transduction of proliferative signals in addition to some survival signals). Mutations Y577F or Y612F abolish signalling and each residue alone is sufficient for STAT5 and Shp phosphorylation. The other tyrosine residues, when individually mutated to phenylalanines, also result in diminished proliferation. Serine 585 is phosphorylated at limiting doses of cytokine and transduces a survival signal. B. The table highlights the various signal transduction cascades that are activated by various regions of the ß#x00DF;c. The references from which this table was compiled are [38-40, 47-49]