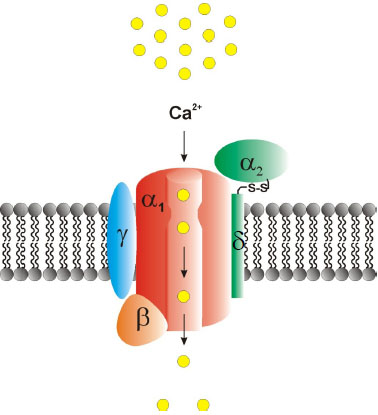
Fig. (1) Structural buildup of voltage-gated Ca2+ channel complexes. Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels are composed of a central pore-forming and ion-conducting α1 subunit as well a variable subset of auxiliary subunits, including α2δ, β and γ-subunits. The β-subunit is located intracellularly whereas the γ and δ subunits are placed within the plasma membrane. The α2 subunit is covalently bound to the δ subunit via a disulfide bond and localized extracellularly. Both the Cav-α1 subunits as well as the auxiliary subunits are important drug targets (reprinted from [68]).