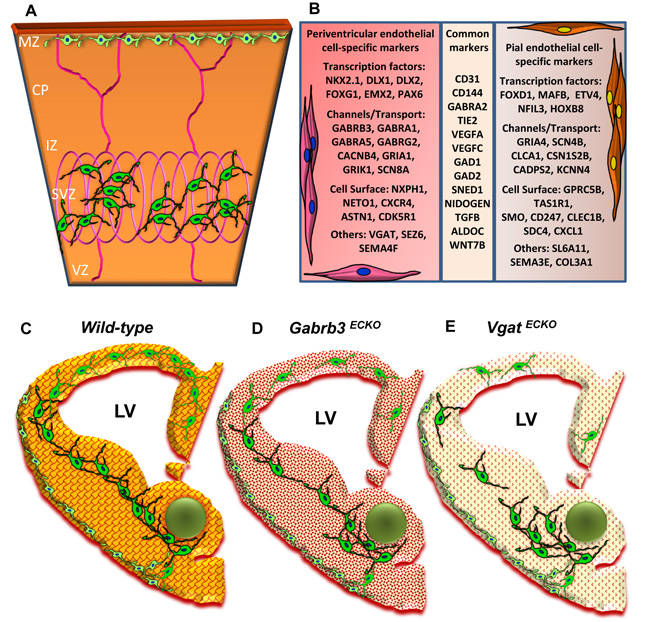
Fig. (3) (A) Schema depicting selective sorting of superficial stream of GABAergic interneurons in the MZ by pial vessels and deep stream of GABAergic interneurons in the SVZ by the periventricular vessels of the embryonic telencephalon [E13]. (B) A table depicting some important markers that distinguish periventricular endothelial cells from pial endothelial cells in the embryonic telencephalon. Common markers expressed in pial and periventricular endothelial cells are also shown. (C-E) Schema depicting conceptual changes in GABA signaling during brain development. (C) Wildtype embryonic telencephalon with normal periventricular vascular network (red lattice pattern) and normal endothelial GABA signaling pathway (reddish-orange hue) promotes tangential GABAergic neuronal migration (green) from the ventral telencephalon. (D) In Gabrb3 ECKO telencephalon, which has dysfunctional endothelial GABAA receptors, there is a partial loss of endothelial GABA secretion (light orange hue). This affects periventricular angiogenesis (intricate red pattern) and neuronal migration with a reduction in GABAergic interneurons in the developing neocortex. (E) In Vgat ECKO telencephalon, there is a complete loss of endothelial GABA secretion (light yellowish hue) that affects periventricular angiogenesis (dotted red pattern) with more significant consequences for GABAergic neuronal migration resulting in abnormal cortical distribution.