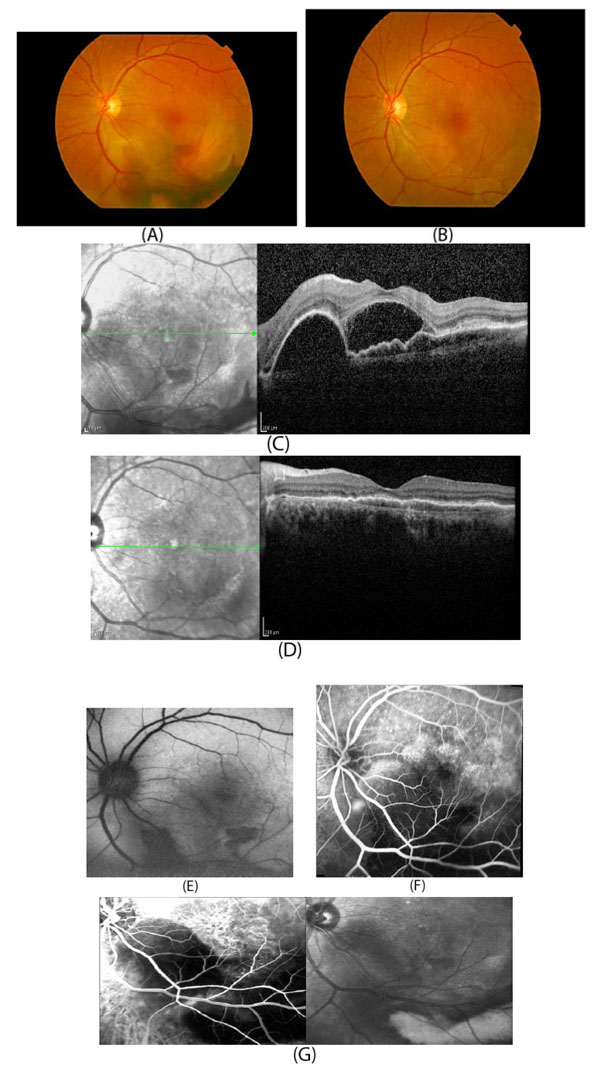
Fig. (4)
Multimodal imaging of a patient with type 1 CNV. Fundus photography (Fig. 4A) shows the subretinal hemorrhage in the lower part of the macula. Fundus photography (Fig. 4B) of the same eye after treatment showing resolution of the subretinal hemorrhage (visual acuity 20/25). OCT image (Fig. 4C) shows subretinal fluid and pigment epithelial detachment with subretinal hyper-reflective material. OCT (Fig. 4D) of the same eye showing resorption of subretinal fluid and pigment epithelial detachment after treatment. Fundus autofluorescence before treatment (Fig. 4E) shows inferior hypoautofluorescence (corresponding to subretinal hemorrhage). Fluorescein angiography before treatment (Fig. 4F) with blockage of fluorescein in the area of subretinal hemorrhage with some superior hyperfluorescence. ICG angiography before treatment (Fig. 4G) shows hypercyanescence in a lacy pattern showing subretinal choroidal neovascularization and hypocyanescence in the area of thick subretinal hemorrhage.