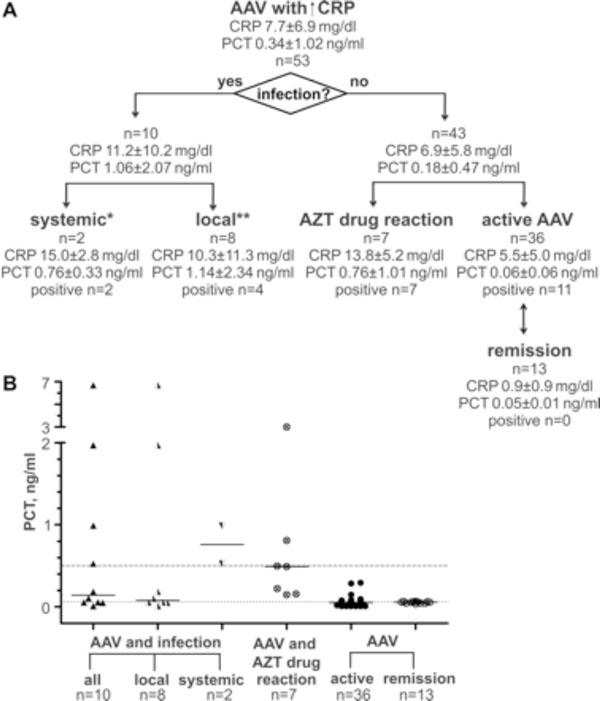
Fig. (1) A: Flowchart of analyzed AAV subgroups. CRP and PCT concentrations are represent as mean and standard deviation. Number of PCT positive samples is given for each subgroup. Additions to infection and causative pathogen: * -recurrent sepsis (blood culture: gram-negative rod-shaped bacteria; urin culture: klebsiella oxytoca);-respiratory sepsis, in course with multiorgan failure and exitus (bronchial lavage: multiresistent pseudomonas aeruginosa, candida albicans, aspergillus fumigatus; blood culture: enteroccus faecium) ** -atypical mycobacteriosis (bronchial lavage: M. avium, M. intracellulare complex);-pneumonia (bronchial lavage: staphylococcus aureus, haemophilus influenzae);-pneumonia (bronchial lavage: haemophilus influenzae); -pneumonia (sputum: escherichia coli, enterococcus faecalis, pseudomonas aeruginosa); -lacrimal duct abscess (MRSA); -serom of parotid gland (enteroccocus); -superinfection of pulmonal cavern (actinobacter and aspergillus); -superinfection of skin ulcus with concomitant lymphadenitis (proteus mirabilis, enterococcus faecalis, stenotrophomonas). B: PCT concentrations in AAV patients. Horizontal line indicates the defined limit for systemic infections at 0.5 ng/ml and functional assay sensitivity at 0.06 ng/ml. Bars are medians. 13 of 36 AAV patients were assessed regarding CRP and PCT levels during active disease and remission.